Narrative is the organization given to a series of facts. The audience can connect events and make interpretations based on those connections. On the contrary of story, narrative is the way the story is related to viewers.
For the audience to analyze a narrative successfully, they need to see how it is constructed worth the use of audio codes, visual codes, structure and the characters.
The same classic narrative can be applied to the horror genre, which is often used in many films of said genre.
There is usually a protagonist that ends up being the hero of the movie. There is the antagonist, which is the villain of the film that disrupts the equilibrium of the story. Normally the hero has to embark on the mission to kill the antagonist or solve the problems to save themselves and others around them.
Narrative themes:
- Revenge
- Survival
- Death and murder
- Religious beliefs
- Supernatural
- Paranormal
Todorov’s narrative theory (linear narrative):
- Equilibrium
- Disruption
- Recognition
- Attempt to repair
- Equilibrium
He discovered that for the narrative to move forward in a chronological order, one action has to follow the other. There has to be a clear beginning, middle, and end. He also proposed that the characters need to be changed in some way throughout the story, and that evolution would be evident by the resolution of the story.
So for a story to be successful according to Tudorov it require:
- actions which change the lives of the characters in the story
- some sort of resolution where the change is registered, which creates equilibrium fpr the characters involved.
- equilibrium
Very often narratives can be subjected into being formulaic. For instance, in the sub-genre of slasher films. They start up with an event that turns the antagonist crazy or because of physiological issues they return to their home town and start preying on teenagers. Usually the teens are immoral and quite dumb. Sometimes there is a survivor remaining that then gets targeted in a sequel that is being nuanced at the end of the film.
To break that formulaic narrative, an unconventional narrative structured can be used such as a non-linear narrative.
A non-linear narrative is the opposite of what Todorov narrative theory covers. With a non-linear narrative the story can move backwards and forwards in time; this can be accomplished by using a flashback technique. A movie that uses this type of narrative structure is Memento by Christopher Nolan. One can see the flashbacks of the main character writing on the Polaroids in black and white contrasting to the present that is in color. The movie could be also considered having a circular narrative, because the movie starts with its ending and the audience can only understand the ending clearly once the film is done.
Narrative codes and conventions:
- Flashback – used to give audiences extra information, normally used to show the past of a character, this storytelling device helps to drive the story further.
- Point of view shots – this type of shots give audiences the same view as a particular character. POV are very effective in horror films because the camera can take the view of the villain stalking a victim.

- Apparently impossible positions – this type of camera shot give out unusual perspectives of action.
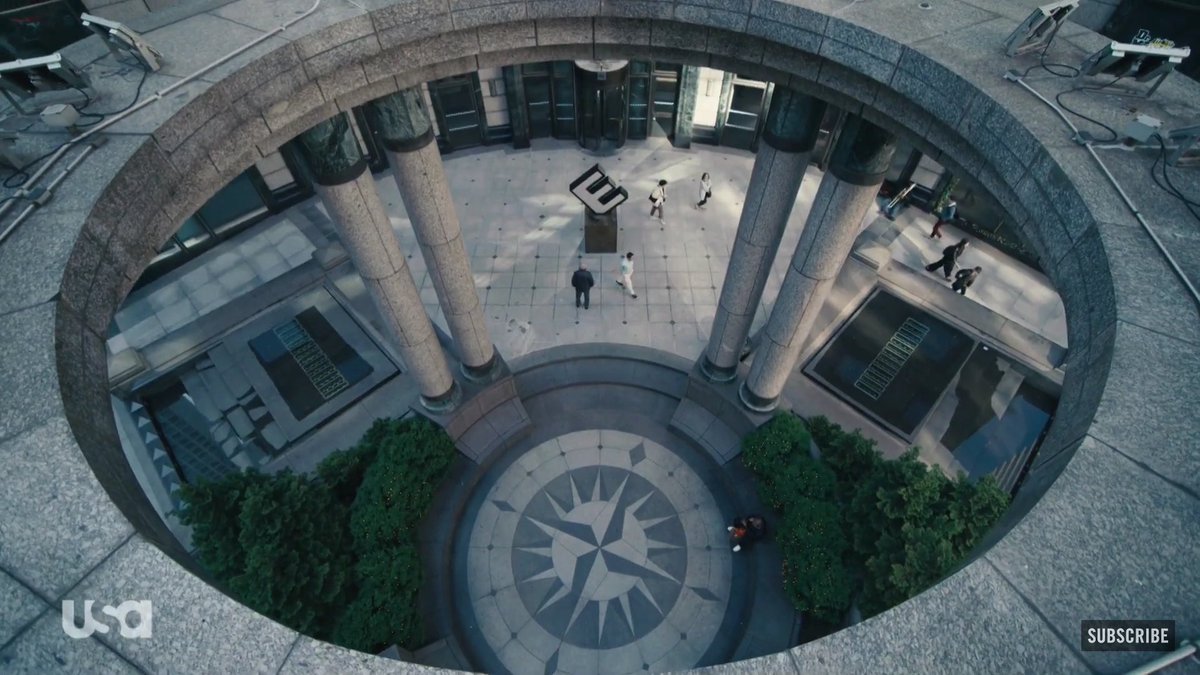

- Privileged spectator positions – the camera places viewers in a position where they see aspects of the narrative that other characters cannot see.
- Voiceovers – can be used to describe the narrative in movies and TV shows. It could also be used to inform the audience of missing information that is not particularly shown on screen.
- Enigma codes – editing technique where it uses the camera to show only some of the narrative, which ends up leaving the audience with a sense of mystery and intrigues them to know where the narrative will go next.
- Action codes – actions in the narrative that alerts the audience about what to expect as the narrative progresses further.
Folklorist Vladimir Propp claimed stories are character driven. Further, he argues that plots develop from the struggles, actions and decisions of characters and how they function in a story. He claimed that characters can be classified into particular roles that progress the story, such as characters like the villain that struggles to detain the hero trying to achieve their quest.

Narrative techniques:
- Time and space – playing and manipulating with time and space could be used while constructing a narrative. Like when live sports can be viewed by multiple people from anywhere in the world
- Multi-stranded – in TV shows and movies the narrative structure don’t always follow the same format or story line. This allows the TV producers to interweave narratives over a series of episodes. By using cliffhangers it encourages the audience to keep to date as the narrative progresses.
- Three strand narrative – introduces three different strands at the start of a TV episode and then links them as the episode progresses.
- Split-screen narratives – the screen splits into sections. Each section shows a mini narrative.
- Flexi-narrative -complex characters surrounding the central plot. Other smaller story lines mix with the original story line. Challenges the audience to question what is real wand whats not, it adds to the mystery.